10 Topics About Networking
1. Basics of Networking
NETWORK — Collection of computers and devices connected together for communication & data exchange between them.
NODES — Devices connected to the Network. Includes computers, servers, printers, routers
Protocols — Set of rules and standards how data is transfer over network like TCP,HTTP,FTP
LAN (LOCAL AREA NETWORK) — Network that covers a very small area
WAN (WIDE AREA NETWORK) — Network that covers a wide area like city, country.
IP Address — Unique Numerical Id for every device on network
Firewall — Monitor and control the inbound and outbound network traffic
2. IPv4 and Subnetting
IPv4 = Internet Protocol version 4
- It uses 32 bit address. It has both public and private IP’s. Starts from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255 approx 4 billion ip address. Inthat 18million address are private.
10.0.0.0 — 10.255.255.255 — (24 bit) Class A — 1,67,77,216
172.16.0.0 — 172.31.255.255 — (20 bit) Class B — 10,48,576
192.168.0.0 — 192.168.255.255 — (16 bit) Class C — 65,536
Subnetting
It is a Network inside the network (dividing larger network into smaller)
To improve Network performance and security subnets are used.
3. FIREWALL
It’s a Network Security Device that monitors and filters inbound and outbound network traffic.
Firewall is the first line of defence in network security.
It can be Hardware, Software, Software as a Service (SaaS), Public Cloud , Private Cloud (virtual)
TYPES OF FIREWALL
PROXY FIREWALL — Filter network in Application layer ,Gateway from one network to another.
PACKET FILTERING — Control data flow
STATEFUL INSPECTION — Allow or Block Network traffic based on state,port and protocol
Next Generation Firewall — Deep pocket Inspection, intrustion prevention
UTM (Unified Threat Management) — Capabilities of stateful inspection, Intrustion Prevention and antivirus in a loosely linked manner
Thread Focused — Advanced Threat detection.
4. Inbound and Outbound rules in Firewall
INBOUND — Protect Network against incoming traffic
OUTBOUND — Project against outgoing traffic
5. DHCP Server
DHCP — Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
It maintains a unique IP address for a host using the server
DHCP also provide DNS(Domain Name System) server
DHCP port numbers used for servers and clients are 67 and 68 respectively
6. DNS Server
Domain Name System (DNS) is the Phonebook of the Internet
Four servers work together to deliver IP address to the Client
DNS Caching — The recursive resolver store the information for a limited amount of time. Meantime host hit the same server instead of doing the domain lookup process, simply respond to the client instantly
Recursive Resolver
Root nameservers
TLD nameservers — Top Level Domain
Authoritative nameservers
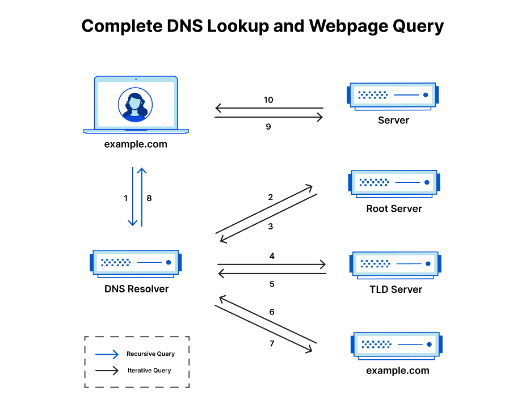
DNS LOOKUP
7. Cloud Flare and How to Use
Cloud Flare — Its a large network of servers that can improve the Security, Performance and Reliability of anything connected to the Internet. Cloud flare is the Content Delivery Network by providing Edge locations.
Performance Improved by providing the Edge Locations. Example: If a cloud flare customer’s server is in USA, if the client access the server in Europe cloud flare provides their servers to reach the client without latency
8. DNS Records
- Provides Information about a domain including what IP address is associated with the domain. DNS Records also have TTL (Time to Live) defines how often DNS Server clear the records
TYPES OF DNS RECORD:
A record — Holds IP Address of the Domain. (IPv4)
AAAA record — Holds IPv6 Address
CNAME record — CNAME (Canonical Name) map one domain to another
MX record — Directs mail to an E-mail server
TXT record — Store text in records
NS record — Store Name Server for DNS entry
SOA record — Stores Admin Information
9. Point DNS Records
Connecting DOMAIN NAME to the Web Host Server
Pointing is the one last steps before server goes live
10. How to Secure Network
Network Access Control — Only Authenticated and trusted endpoint devices can get into the system.
Firewall Security — Monitor and filters the incoming and outgoing network traffic. It follows defined rules of IP address and ports to allow or deny traffic
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) — Identify and Prevent unusual network traffic. Its does not follow any static rules like firewall but actively analyze, learn and create rules. EXAMPLE: If Firewall is your Building Security Gate, IPS is like your security guard behind the gate
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) -It sends out reports on security-related events like failed logins and sends out alerts if its analysis indicates a potential security issue